Nitrogen use efficiency in upland rice on an acid soil in western Guarico state
Abstract
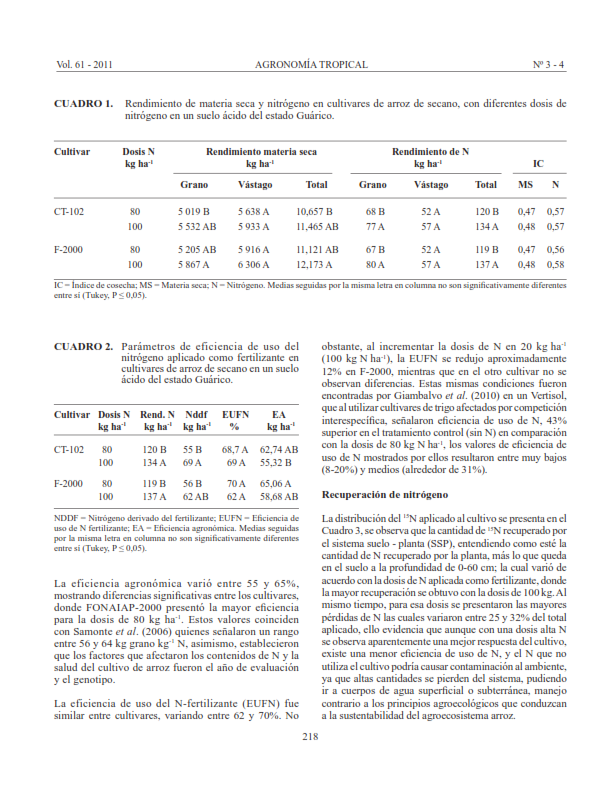
In order to evaluate absorption efficiency, agronomic use and recovery of N in rainfed rice, Oryza sativa L., cultivars in soil acid condition (acid Kandic Plinthustults), a field experiment was carried out using two cultivars, the CT-102 and FONAIAP-2000 (F-2000) at southeastern of Guárico State. The experimental design was a randomized block with three replications. The doses of nutrients (kg ha-1) were 80-100 N, 80 P and 80 K, was used urea, diammonium phosphate, and potassium chloride as nutritional sources. 15N-urea (5 atom% excess) was used in the isotopic micro plots. At the moment of harvest samples were taken of soil and plant (crop and weed) for chemical determinations, were calculated the efficiency of use of nitrogen fertilizer (EUFN), agronomic efficiency (EA) and harvest index (IC). Grain yield ranged from 5.0 to 5.9 t ha-1 significantly higher in F-2000. between cultivars were not observed statistical differences for EUFN and IC. Although were observed significant differences statistical for N derived from fertilizer and EA. The highest grain yield and N efficiency were observed in F-2000 with high potential to be used in soil acid. The results also show that although the crop had a better response with higher doses of N, efficiency use of N tends to decrease, implying that excess of nitrogen removed of the soil-plant system could cause more environmental pollution.
Downloads
References
• Carrillo de Cori, C. E., E. Casanova y G. Rico. 1992. Balance de Nitrógeno en arroz de riego en un vertísol del estado Guárico. Agronomía Trop. 42:67-84.
• Craswell, E. T. and D. C. Godwinn. 1984. The efficiency of nitrogen fertilizers applied to cereals grown in different climates. In: Tinker P.B. Lauchli A: (Eds.) Advances in Plant Nutrition 1:1-56.
• Comerma, J. 2009. Suelos mal drenados en Venezuela. Agronomía Trop. 59(1):25-32.
• FAO. 2004. FAOSTAT. Consultado en: www.fao.org. com. Disponible en línea: agosto 2009.
• Giambalvo, D., P. Ruisi and G. Di Micelli. 2010. Nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen fertilizer recovery of durum wheat genotypes as affected by interspecific competition. Agron. J. 102(2):707-715.
• Gilabert de Brito, J., I. López de Rojas y R. Roberti. 1990. Análisis de suelo para diagnóstico de fertilidad. In: Manual de métodos y procedimientos de referencia. FONAIAP-CENIAP. Maracay. Cap.4.1-5.1 (Serie. D.Nº 26).
• IAEA. 2001. Use of isotope and radiation methods in soil and water management and crop nutrition, Vienna. IAEA-TCS-14.
• INFOSTAT. 2004. Infostat versión 1 2004 grupo infostat, F C.A, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. 200 p.
• Kjeldahl, J. 1983. A new method for the determination of nitrogen organic matter. 2. Analytical Chemistry 366 p.
• Rey, J. C. 2002. Informe caracterización de suelos experimentales ubicados en el municipio Francisco de Miranda, estado Guárico. INIA-Guarico 6 p.
• Samonte, S. O. P. B., L. T. Wilson, J. C. Medley, S. R. M. Pinson, A. M. McClung and J. S. Lales. 2006.
• Nitrogen utilization efficiency: Relationships with grain yield, grain protein y yield-related traits rice. Agron. J. 98:168-176.
• Sanabria D., T. Rodríguez, F. Barreto y A. Torres. 1999. Arroz de secano: otra alternativa evaluada por FONAIAP para la diversificación de la producción en los Llanos Orientales de Venezuela. Consultado en: https://bit.ly/2QD6Uw8
• Timsina J., U. Singh, M. Badaruddin, C. Meisner and M. R. Amin. 2001. Cultivar, nitrogen, and water effects on productivity and nitrogen-use efficiency and balance for rice-wheat sequences of Bangladesh. Field Crop. Res.72:143-161.
• Tirol-Padre, A., J. K. Ladha, U. Singh, E. Laureles, G. Punzalan and S. Akita. 1996. Grain yield performance of rice genotypes at sub-optimal levels of soil N as affected by N uptake and utilization efficiency. Field Crop. Res. 46:127-143.
• Urquiaga, S. y F. Zapata. 2000. Manejo eficiente de la fertilización nitrogenada de cultivos anuales en América Latina y el Caribe. Porto Alegre; Génesis; Río de Janeiro. EMBRAPA Agrobiología 110 p.
• Worku, M., M. Banziger, G. S. auf´m Ealey, D. Friesen, A. O. Diallo and W. J. Horst. 2007. Nitrogen uptake and utilization in contrasting nitrogen efficient tropical Maize hybrids. Crop Sci. 47:519-527.