Evaluación de la inducción de variabilidad genética en cambur 'manzano' (Musa AAB) a través de marcadores RAPD
Resumo
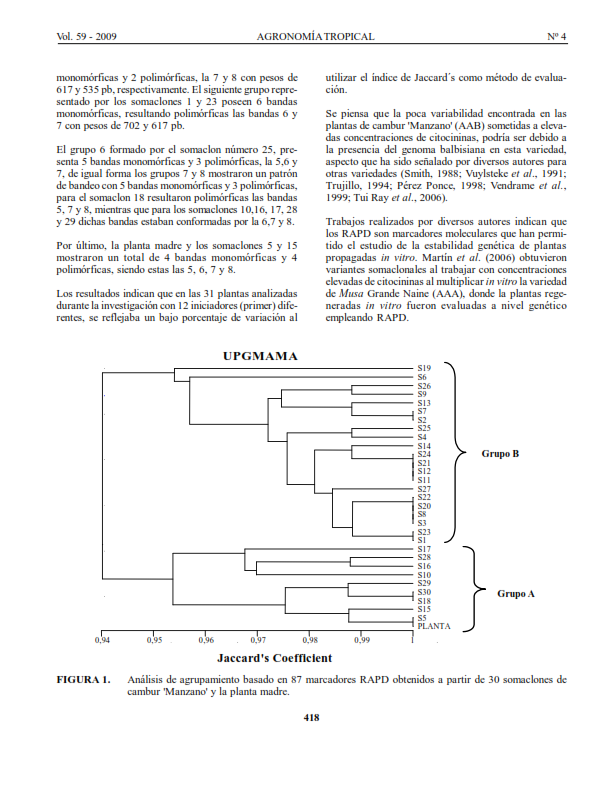
En Venezuela, el cambur 'Manzano' (Musa AAB, banano tipo manzano) posee amplia aceptación por parte de los consumidores, pero su comercialización se ha visto limitada por el alto índice de plagas y enfermedades que lo atacan. En este sentido, el uso de las técnicas para el mejoramiento de la especie han tenido gran auge, por lo que en esta investigación se realizó la inducción de variación somaclonal mediante el uso de elevadas concentraciones de citocininas a través de multiplicaciones sucesivas, durante las cuales se aumentó de manera paulatina dichas concentraciones (5-10-15 mg l-1 de BA, respectivamente). Para el análisis de las plantas obtenidas de esta experiencia, se utilizó la técnica de los RAPD (ADN polimórfico amplificado al azar), la cual permitía establecer un patrón de comparación entre las plantas que se sometieron al proceso de inducción de variación somaclonal. Los resultados indican que en las 31 plantas analizadas durante la investigación con 12 iniciadores (primer) diferentes, se reflejaba un bajo porcentaje de variación al utilizar el índice de Jaccard´s como método de evaluación. Se piensa que la poca variabilidad encontrada en las plantas de Cambur Manzano (AAB) sometidas a elevadas concentraciones de citocininas, se debe a la presencia del genoma balbisiana en esta variedad, aspecto que ha sido señalado por diversos autores para otras variedades.
Downloads
Referências
• Cárdenas, J. E, L. Pocasangre, A. S. Riveros y F. Rosales. 2002. Selección temprana de vitroplantas de Gros Michel (AAA) resistentes a la raza 1 del Mal de Panamá (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense). Memoria del II Encuentro de Investigadores en Agricultura Orgánica. 18 p
• Cloutier, S. and B. S. Landry. 1994. Molecular Markers Applied to Plant Tissue Culture. In vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 30:32-39.
• Crouch, H. K., J. H. Crouch, S. Madsen, D. R, Vuylsteke and R. Ortiz. 2000. Comparative analysis of phenotypic and genotypic diversity among planta in landrace (Musa spp., AAB, group). Theoretical and Applied Genetics 101(7):1 056-1 065.
• Doyle, J. J. and J. L. Doyle. 1990. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissues. Focus 12:13-15.
• Duncan, R. 1997. Tissue Culture-Induced variation and crop improvement. Advances in Agronomy. 58:201-240.
• Escalante, J. V., A. Tapia y J. Sandoval. 1989. Inducción de Callos Suspensión de Células y posibilidades de Regeneración en Musa sp. previa presión de Selección. In: Memorias de la IX reunión de ACORBAT, Mérida, Venezuela. p. 35-42.
• Fauré, S., J. L. Noyer, J. P. Horry, F. Bakry, C. Lanaud and D. Gonzalez de Leon. 1993. A molecular marker- based linkage map of diploid bananas (Musa acuminata). Theor. Appl. Genet. 87:517-526.
• Gawel, N. J., R. L. Jarret and A. P. Whittemore. 1992. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)- Based Phylogenetic Analysis of Musa. Appl.Genet. 84:286-290.
• Giménez, C., E. de Garcia, N. Xena de Enrech and I. Blanca. 2001. Somaclonal Variation in banana: cytogenetic and molecular characterization of the somaclonal variant CIEN BTA-03. In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.Plant 37:217- 222.
• Haddad, O. y O. Borges. 1974. Los Bananos en Venezuela: Estudio y Descripción de Clones de Plátano y Cambur. Dirección de Investigación. Ministerio de Agricultura y Cría. 105 p.
• Haddad, O. y F. Leal. 1996. Situación actual y perspectivas de la producción de cambur de exportación y otras Musáceas en el estado Aragua. Fundación para el Desarrollo de la Ciencia y la Tecnología en el es t a do de Ar a gu a . [en línea ]. Dis p onib le en www.fundacite.arg.gov.ve./papelesf/index.html.
• Kahangi E., M., M. A. Lawton, C. A. Kumar. 2002. RAPD profiling of some banana varieties selected by small-scale farmers in Kenya. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 77(4):393-398.
• Larkin, P. and W. Scowcroft. 1981. Somaclonal variation a novel source of variability from cell cultures from plant improvement. T heor. Appl. Genet. 60:197-214.
• Martin, K. P., S. K. Pachathundikandi, C. I. Zhang, A. Slater and J. Madassery. 2006. RAPD analysis of a variant of banana (Musa sp.) cv. Grande Naine and its propagation via shoot tip culture. In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 42:188-192.
• Munthali, M., H. J. Newbury and B. V. Ford-Lloyd. 1996. The detection of somaclonal variants of beet using RAPD. Plant Cell Rep. 15:474-478.
• Murashige, T. y F. Skoog. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiology Plantarum. 15: 473-497.
• Orellana, P, J. Pérez-Ponce, D. Agramonte, R. Gómez, E. Jiménez, S., Martínez, E. Almaguer y P. Gómez. 1991. La micropropagación del plátano a escala comercial en Cuba. Universidad central de Las Villas. Cuba 8 p.
• Pillay, M., D. C. Nwakanma and A. Tenkouano. 2000. Identification of RAPD marker linked to A and B
genome sequences in Musa L. Genome 43(5):763-767.
• Pérez Ponce, J. 1992. Variación Somaclonal. Primer curso FAO-Francia-Cuba, sobre técnicas modernas de mejora miento y mult iplicación de esp ecies agámicas. U.C.L.V. Cuba. S/P.
• Salazar, E., J. G. Surga, J. A. Landínez y I. Trujillo. 2006. Uso de RAPD para la caracterización molecular de genotipos de Musa AAA propagados in vitro. Memorias de la Reunión Internacional ACORBAT 2006. Vol 2. p. 484.
• Sánchez, I. 2002. Búsqueda y aislamiento de marcadores moleculares en Pleurotus ostreatus. (En línea). Navarra, España. (Consultado 1 ago. 2002). Disponible en https://bit.ly/3jOpEFW
• Smith, M. K. 1988. A review of factors influencing the genetic stability of micropropagated bananas. Fruits 43:219-223
• Surga, J. 1988. Obtención de plantas libres de Virus de Mosaico del pepino por cultivos de ápices meristemáticos aislados in vitro de dos cultivares de banano. Fitopatología Venezolana. 1(2):69-72.
• Tingey, S. V., J. A. Rafalski and J. G. K. Williams. 1994. Genetic Analysis with RAPD Markers. In: Aplications of RAPD Technology to Plant Breeding. Minneapolis. Minnesota. p. 3-8.
• Trujillo, I. 1994. Aplicación de Técnicas Biotecnológicas en el Mejoramiento del género Musa. Tesis Doctoral. Universidad Central de Venezuela. Escuela de Biología. Dto. de Botánica.
• Trujillo, I. and E. de García. 1996. Aplicación de métodos de presión de selección en la obtención de variantes de banano resistentes a la Sigatoka amarilla. Phyton 59: 111-121.
• Tui, Ray, D. Indrajit, S.Prasenjit, D. Sampa and S. C. Roy. 2006. Genetic stability of three economically important micropropagated banana (Musa spp.) cultivars of lower Indo-Gangetic plains, as assessed by RAPD and ISSR markers. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. 85:11-21
• Vidal, M. 1996. Análisis bioquímico y genético de somaclones de Musa sp. obtenidos mediante procesos de cultivo in vitro. Universidad Central de Venezuela. Escuela de Biología. Dpto. de Botánica.
• Vendrame, W. A, G. Kochert and H. Y. Wetzstein. 1999. AF LP a nalys is of var iat ion in peca n s omat ic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 18:853-857
• Venkatachalam, I., R. V. Sreedhar and N. Bhagyalakshmi. 2007. Genetic analyses of micropropagated and regenerated plantlets of banana as assessed by RAPD and ISSR markers. In vitro Cell.Dev.Biol. Plant 43:267-274.
• Vuylsteke, D., R. Swennen and E. De Langhe. 1991. Somaclonal variation in plantains (Musa spp., AAB group) derived from shoot tip culture. Fruits 46:429-439.
• Williams, J. G. K., A. R. Kubelik, K. J. Livak, J. A. Rafalski and S. V. Tingey. 1990. ADN Polymorphisms amplified by Arbitrary Primers are Useful as Genetic Markers. Nucleic Acids Research. 18(22):6 531-6 535.