Embriogénesis somática a partir de flores masculinas de pineo gigante y cambur manzano
Resumo
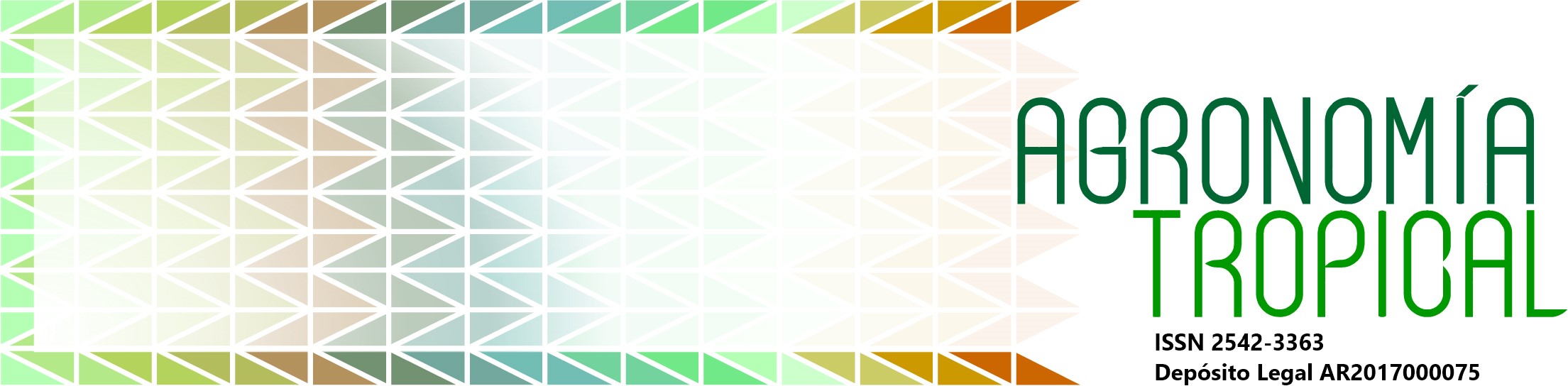
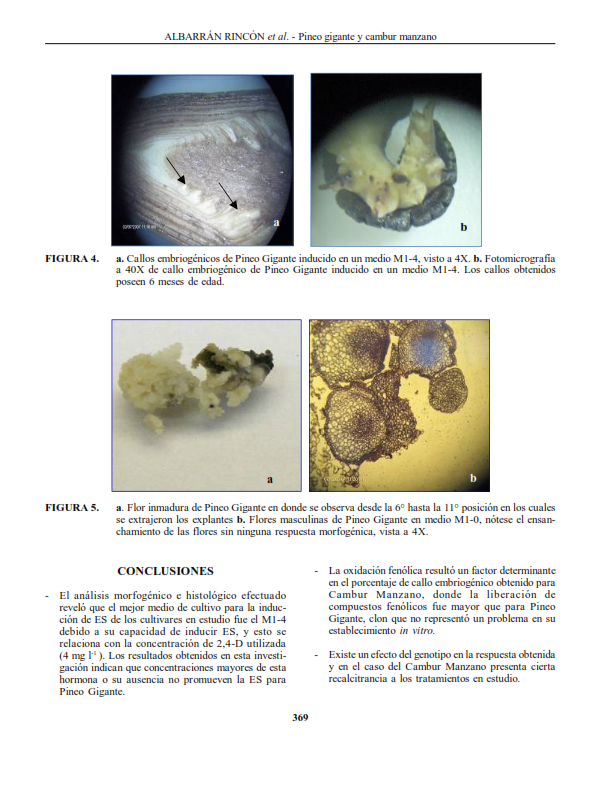
El banano es importante en Venezuela y en países tropicales por su contenido de vitaminas y minerales. La demanda de cultivares mejorados con resistencia a enfermedades, hace recurrir a métodos biotecnológicos. El objetivo del trabajo fue inducir la embriogénesis somática (ES) y suspensiones celulares, mediante el cultivo in vitro de flores masculinas inmaduras, en los cultivares Pineo Gigante, Musa AAA y Cambur Manzano, Musa AAB. Se seleccionaron flores entre las posiciones 6a y 11a de la yema floral reducida; para la ES se utilizó un medio de cultivo MS suplementado con biotina 1 mg l-1, extracto de malta 0,1 g l-1, glutamina 10 g l-1, AIA 1 mg l-1 ANA 1 mg l-1, 2,4-D (0, 2, 4 y 8 mg l-1) y agarosa 7 g l-1. Para la suspensiones celulares se usó el medio MS1 suplementado con 2,4-D 3 mg l-1, caseína hidrolizada 0,4 g l-1, azúcar 20 g l-1 y el MS2 suplementado con caseína hidrolizada 0,4 g l-1, agua de coco 50 ml l-1, 2,4-D 3 mg l-1, arginina 50 mg l-1 y azúcar 30 g l-1. Se realizó un estudio histológico para el cultivo inicial, callogénesis y ES. En el cultivar Pineo Gigante se obtuvieron callos friables con embriones en estado globular, evidenciado histológicamente, a los 6 meses de cultivo y suspensiones celulares 2 meses después. En Cambur Manzano se obtuvo callogénesis e inducción de ES en el medio MS-4 siempre en menor proporción que lo obtenido para Pineo Gigante. En Manzano, no se formaron suspensiones celulares.
Downloads
Referências
• Castillo, E. 2003. Proliferación de yemas para la embriogénesis somática en tres variedades de Musa. Tesis de Pregrado. San Juan de Los Morros. Venezuela. Universidad Experimental Rómulo Gallegos. 60 p.
• Côte, F., R. Domergue, S. Monmarson, J. Schwendiman, C. Teisoon and J. Escalant. 1996. Embryogenic cell suspensions from the male flower of Musa AAA cv. Grand nain. Physiologia Plantarum 97:285-290.
• Escalant, J., C. Teisson and F. Côte. 1994. Amplified somatic embryogenesis from male flowers of triploid banana and plantain cultivars (Musa spp.). In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30P: 181-186.
• Escalant, J. y J. Sandoval. 1989. Inducción de callos, suspensión de células y posibilidades de regeneración en Musa sp. previa presión de selección. In: 9na Reunión de la Asociación para la Cooperación en Investigaciones de Banano en El Caribe y América Tropical. Resúmenes, Mérida, Venezuela. p. 35-42.
• Grapin, A., J. Ortíz, R. Domergue, J. Babeau, S. Monmarson, J. Escalant C. Teisson y F. Côte. 1998. Obtención de callos embriogénicos, iniciación y regeneración de suspensiones celulares embriogénicas a partir de flores inmaduras masculinas y femeninas de Musa. INFOMUSA. 7(1):13-15.
• Haicour, R., V. Bui Trang, D. Dhed’a, A. Assani, F. Bakry and F. X. Cote. 1998. Banana improvement through biotechnology-ensuring food security in the 21st century (Abstract in English). Cahiers Agricultures: 468-475. Houllou-Kido, L., E. Kido, M. Falco, M. Silva, A.
• Jamaluddin, S ., and F. Nova K. 1992. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of banana cultivars, Musa cv. Mas (AA) and Musa cv. Rastali (AAB). In: Proceeding: International Symposium on Recent Development in Banana Cultivation Technology (Valmayor RV y col eds). INIBAP/ ASPNET. Los Baños. Filipinas. pp. 201-212.
• Khalil, S., K. Cheah, E. Pérez and D. Gaskill. 2002. Regeneration of banana (Musa spp. AAB cv. Dwarf Brazilian) via secundary somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell REp. 20: 1128-1134.
• Krikorian, A. 1986. Callus and cell culture, somatic embryogenesis, androgenesis and related tecniques for Musa improvement. Proceedings of an International Workshop held at Cairns. INIBAP. Camberra. 21:128-135.
• Liu, J., E. Rosa, E. Lizardi, A. Arocho, N. Díaz y J. A. Rodríguez, 1989. In vitro Propagation of Plantain (Musa acuminata x M. balbisiana AAB) and banana (M. acuminata AAA) in Puerto Rico. Journal of Agricult ure of the University of Puer to Rico. 73(1):51-58.
• Murashige, T. and F. Skoog. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15:473-490.
• Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Agricul- tura y la Alimentación (FAO). 2007. FAOSTAT. [En línea]. Datos estadísticos de consumo calórico de los principales cultivos en Venezuela. [Consultado: 03.03.2007]. [Disponible:] https://bit.ly/2CMKeWT
• Ramírez, M. 1998. Tratamientos a plantas madres y al explante para el establecimiento in vitro del guayabo (Psidium guajava L.). Trabajo de Grado. Maracaibo, Ven. La Universidad del Zulia. Facultad de Agronomía. División de Est udios para Graduados. Programa Fruticultura. Venezuela. 132 p.
• Ramírez, M., E. García and H. Finol. 2006. Ultrastructural studies on embryogenic and non embryogenic calluses from Williams’ banana (Musa spp.). Agronomía Trop. 56(4):615-620.
• Roth, I. 1964 . Microtécnica Vegeta l. Es cuela de Biología. Caracas. Universidad Central de Venezuela. Facultad de Ciencias. 88 p.
• Schoofs, H. 1997. The origin of embryogenic cells in Musa. Dissertationes de Agricultura 330. Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium. 257 p.
• Strosse, H., R. Domergue, B. Panis, J. V. Escalant and Côte; F. 2003. Suspensiones de células embriogénicas de banano y plátano (A. Vézina y C. Picq, eds). Guías técnicas INIBAP 8. Red Internacional para el Mejoramiento del Banano y el Plátano, Montpellier, Francia. 36 p.
• Trujillo, I. and E. García. 1999. Somatic embryogenesis in vitro of Musa clones. PHYTON 64:7-17.
. Vargas, N. Nogueira, M. Lanzoni and A. Tulmann. 2005. Somatic embryogenesis and the effect of particle bombardment on banana Maçã regeneration. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira. 40(11):1 081-1 086.
• Vidal, M., T. Vargas y E. García. 2000. Estudios anatómicos y morfológicos de la iniciación de embriones somáticos obtenidos a partir de ápices meristemáticos de Musa spp. Acta científica Venezolana. 51(2):78-83.
• Villegas, F. Z., A. C. Giménez, P. J. Vilchez, M. Moreno, L. Sandoval y M. Colmenares. 2008. Oxidación en la inducción de la embriogénesis somática a partir de flores masculinas inmaduras de Gran Enano (Musa AAA). Rev. Fac. Agron. 25(3):